Q:
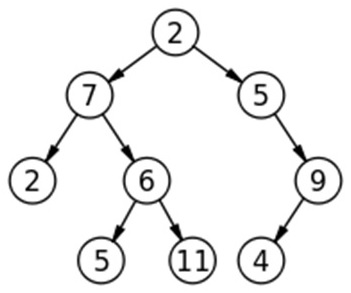
Given a Binary Tree and a number K. Print all nodes that are at distance K from root (root is considered at distance 0 from itself)
belongs to collection: Interview C++ coding problems/challenges | tree
Interview C++ coding problems/challenges | tree
- Find the level in a binary tree with given sum K
- Check whether a Binary Tree is BST (Binary Search Tree) or not
- Print vertical sum of a binary tree
- Print Boundary Sum of a Binary Tree
- Given a Binary Tree T and a sum S, write a program to check whether there is a root to leaf path in that tree with the input sum S
- Given a Binary Tree write a program to print the nodes which don’t have a sibling node. Print all the nodes separated by space which do not have sibling in the tree in sorted order if every node has a tree than print -1
- Given a Two Binary Trees, write a function that returns true if one is mirror of other, else returns false
- Given a Binary Tree where each node has positive and negative values. Convert this to a tree where each node contains the sum of the left and right sub trees in the original tree. The values of leaf nodes are changed to 0
- Given a binary Tree, check whether the tree is symmetric or not
- Write a program to print Reverse Level Order Traversal of a binary tree
- Given an array where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST. For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1
- Given a Binary Tree, write a function getLevelDiff which returns the difference between the sum of nodes at odd level and the sum of nodes at even level
- Write a function to detect if two trees are isomorphic
- Given an expression tree evaluate the expression tree
- Given a Binary Tree and a number K. Print all nodes that are at distance K from root (root is considered at distance 0 from itself)
- Given a Binary Tree, print Right view of it. Right view of a Binary Tree is set of nodes visible when tree is visited from Right side
- Given a Binary Tree, find diameter of it. The diameter of a tree is the number of nodes on the longest path between two leaves in the tree
- Given a BST and a value x, write a function to delete the nodes having values greater than or equal to x. The function will return the modified root
- Given a binary tree, print the diagonal traversal of the binary tree
- Given a Binary Tree, Print the corner nodes at each level. The node at the leftmost and the node at the rightmost
- Given a Binary Search Tree and 2 nodes value n1 and n2, your task is to find the lowest common ancestor of the two nodes. Assume that n1 and n2 both existing node value of the tree
- Given a string that contains ternary expressions. The expressions may be nested. You need to convert the given ternary expression to a binary Tree and return the root
- Given a binary tree, print the bottom view from left to right
- Given a Binary Tree and a target key, write a function that prints all the ancestors of the key in the given binary tree
- Given a Binary Tree of size N, write a program that prints all the possible paths from root node to the all the leaf node\'s of the binary tree
- Given a binary tree, where every node value is a number between 0-9. Find the sum of all the numbers which are formed from root to leaf paths
- Given a binary tree, and two node values your task is to find the minimum distance between them
- Find the k-th smallest element in a given binary search tree (BST)
- Write a program to print Level Order Traversal in spiral form of a binary tree
- Given a binary Tree find the maximum path sum. The path may start and end at any node in the tree
- Given an array pre[] of N nodes representing preorder traversal of BST. The task is to print its postorder traversal
- Given two n-ary trees, the task is to check if they are mirrors of each other or not
- Find number of nodes in a complete Binary Tree




 C++ programming
C++ programming
The above problem can be solved using level order traversal. For every level traversed, keep decrementing K.
Algorithm
Pre-requisite:
A Queue, input binary tree, input K
C++ implementation:
Output
Example with explanation
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer