Explanation
In this program, we need to search a given node in a doubly linked list.
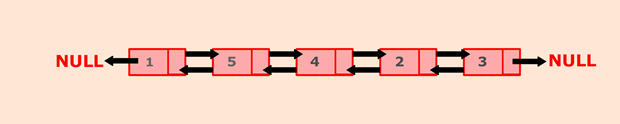
To solve this problem, we will traverse through the list using a node current. Current points to head and start comparing searched node data with current node data. If they are equal, set the flag to true and print the message along with the position of the searched node.
For, eg. In above list, a search node says 4 can be found at the position 3.
Algorithm
- Define a Node class which represents a node in the list. It will have three properties: data, previous which will point to the previous node and next which will point to the next node.
- Define another class for creating a doubly linked list, and it has two nodes: head and tail. Initially, head and tail will point to null.
- addNode() will add node to the list:
- It first checks whether the head is null, then it will insert the node as the head.
- Both head and tail will point to a newly added node.
- Head's previous pointer will point to null and tail's next pointer will point to null.
- If the head is not null, the new node will be inserted at the end of the list such that new node's previous pointer will point to tail.
- The new node will become the new tail. Tail's next pointer will point to null.
- searchNode() will search for a node in the list:
- Variable i will keep track of the position of the searched node.
- The variable flag will store boolean value false.
- Current will point to head node.
- Iterate through the loop by incrementing current to current.next and i to i + 1.
- Compare each node's data with the searched node. If a match is found, set flag to true.
- If the flag is true, prints the position of the searched node.
- Else, print the message "Element is not present in the list".
Input:
#Add nodes to the list
dList.addNode(1);
dList.addNode(5);
dList.addNode(4);
dList.addNode(2);
dList.addNode(3);
Output:
Node is present in the list at the position : 3
Node is not present in the list
Python
Output:
C
Output:
JAVA
Output:
C#
Output:
PHP
Output: