Explanation
In this program, we need to create a singly linked list and display all the nodes present in the list.
Singly Linked List
The singly linked list is a linear data structure in which each element of the list contains a pointer which points to the next element in the list. Each element in the singly linked list is called a node. Each node has two components: data and a pointer next which points to the next node in the list. The first node of the list is called as head, and the last node of the list is called a tail. The last node of the list contains a pointer to the null. Each node in the list can be accessed linearly by traversing through the list from head to tail.
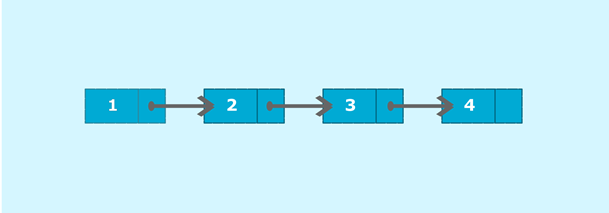
Consider the above example; node 1 is the head of the list and node 4 is the tail of the list. Each node is connected in such a way that node 1 is pointing to node 2 which in turn pointing to node 3. Node 3 is again pointing to node 4. Node 4 is pointing to null as it is the last node of the list.
Algorithm
- Create a class Node which has two attributes: data and next. Next is a pointer to the next node.
- Create another class which has two attributes: head and tail.
- addNode() will add a new node to the list:
- Create a new node.
- It first checks, whether the head is equal to null which means the list is empty.
- If the list is empty, both head and tail will point to the newly added node.
- If the list is not empty, the new node will be added to end of the list such that tail's next will point to the newly added node. This new node will become the new tail of the list.
- display() will display the nodes present in the list:
- Define a node current which initially points to the head of the list.
- Traverse through the list till current points to null.
- Display each node by making current to point to node next to it in each iteration.
Input:
#Add nodes to the list
sList.addNode(1);
sList.addNode(2);
sList.addNode(3);
sList.addNode(4);
Output:
Nodes of singly linked list: 1 2 3 4
Python
Output:
C
Output:
JAVA
Output:
C#
Output:
PHP
Output: