In this program, we need to convert given binary tree to a corresponding binary search tree. A tree is said to be the binary tree if each of the nodes has at most two children. Whereas, the binary search tree is the special case of the binary tree in which all the nodes to the left of root node should be less than root node and nodes to the right should be greater than root node.
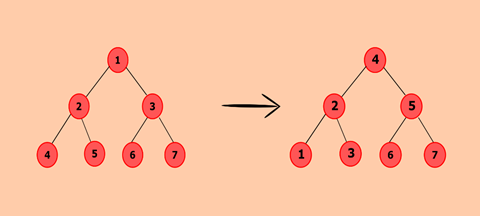
This problem can be resolved by converting given binary tree to its corresponding array representation. Sort the array. Calculate the middle node from array elements as it will become the root node of the corresponding binary search tree.
Algorithm
- Define Node class which has three attributes namely: data left and right. Here, left represents the left child of the node and right represents the right child of the node.
- When a node is created, data will pass to data attribute of the node and both left and right will be set to null.
- Define another class which has two attribute root and treeArray.
- Root represents the root node of the tree and initializes it to null.
- treeArray will store the array representation of the binary tree.
a. convertBTBST() will convert binary tree to the corresponding binary search tree:
- It will convert the binary tree to corresponding array by calling convertBTtoArray().
- Sort the resultant array from step 1 in ascending order.
- Convert the array to the binary search tree by calling createBST().
- calculateSize() will count the number of nodes present in the tree.
- convertBTtoArray() will convert binary tree to its array representation by traversing the tree and adding elements to treeArray.
- createBST() will create a corresponding binary search tree by selecting a middle node of sorted treeArray as it the root node. treeArray will be divided into two parts i.e [0, mid-1] and [mid+1, end]. Recursively find middle node from each array to create left subtree and right subtree respectively.
- Inorder() will display the nodes of the tree in inorder fashion, i.e., left child followed by root node followed by the right child.
Program:
Output: