In this program, we need to create a binary search tree, delete a node from the tree, and display the nodes of the tree by traversing the tree using in-order traversal. In in-order traversal, for a given node, first, we traverse the left child then root then right child (Left -> Root -> Right).
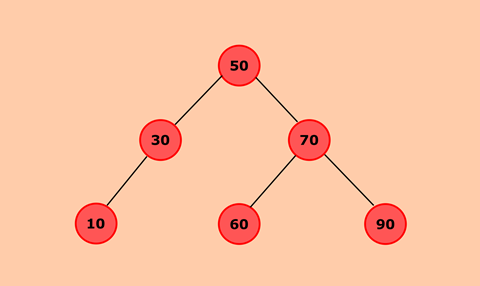
In Binary Search Tree, all nodes which are present to the left of root will be less than root node and nodes which are present to the right will be greater than the root node.
Insertion:
- If the value of the new node is less than the root node then, it will be inserted to the left subtree.
- If the value of the new node is greater than root node then, it will be inserted to the right subtree.
Deletion:
- If the node to be deleted is a leaf node then, parent of that node will point to null. For eg. If we delete 90, then parent node 70 will point to null.
- If the node to be deleted has one child node, then child node will become a child node of the parent node. For eg. If we delete 30, then node 10 which was left child of 30 will become left child of 50.
- If the node to be deleted has two children then, we find the node(minNode) with minimum value from the right subtree of that current node. The current node will be replaced by its successor(minNode).
Algorithm
- Define Node class which has three attributes namely: data, left and right. Here, left represents the left child of the node and right represents the right child of the node.
- When a node is created, data will pass to the data attribute of the node and both left and right will be set to null.
- Define another class which has an attribute root.
- Root represents the root node of the tree and initializes it to null.
a. insert() will insert the new value into a binary search tree:
- It checks whether root is null, which means tree is empty. New node will become root node of tree.
- If tree is not empty, it will compare value of new node with root node. If value of new node is greater than root, new node will be inserted to right subtree. Else, it will be inserted in left subtree.
a. deleteNode() will delete a particular node from the tree:
- If value of node to be deleted is less than root node, search node in left subtree. Else, search in right subtree.
- If node is found and it has no children, then set the node to null.
- If node has one child then, child node will take position of node.
- If node has two children then, find a minimum value node from its right subtree. This minimum value node will replace the current node.
Program:
Output: