In this section, we will learn what is a bouncy number and also create Java programs to check if the given number is bouncy. The bouncy number program frequently asked in Java coding tests and academics. Before understanding the bouncy number, first, we will understand what is increasing and decreasing numbers.
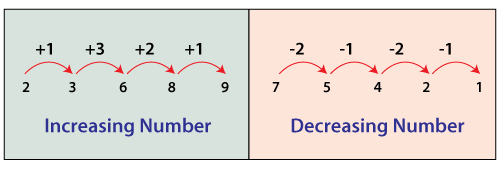
Increasing Numbers
In an integer traversing from left to right if the current digit is greater than or equal to the previous digit, the number is known as increasing numbers. In other words, we can say that if no digit is exceeded by the digit to its left is called increasing numbers. For example, 1233, 13689, 112334566, etc.
Decreasing Numbers
In an integer traversing from left to right if the current digit is less than the previous digit, the number is known as decreasing numbers. In other words, we can say that if no digit is exceeded by the digit to its right is called decreasing numbers. For example, 321, 88531, 8755321, etc.
Let's move to the bouncy number.
Bouncy Number
A positive integer that is neither in increasing nor decreasing number is called a bouncy number. It means they bounce between increasing and decreasing. In other words, we can say that if the digits of the number are unsorted.
For example, 123742, 101, 43682, etc. We observe that in the given number's digits are neither increasing nor decreasing if we traverse from left to right, hence they are called bouncy numbers.
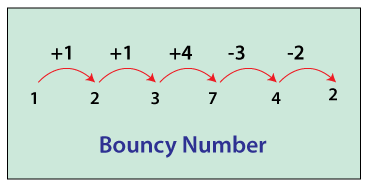
Note that there is no bouncy number between 1 to 100. The first bouncy number is 101.
Steps to Find Bouncy Number
- Read or initialize a number N.
- Convert the given number into a string and store the string in variable str.
- Initialize a flag with true value.
- Start moving from left to right character by character by using a for loop and do the following:
- Define a method with the name isIncreasing(). It checks if any digit is greater than or equal to the next digit. If yes, set the flag to false and exit from the loop.
- Define another method with the name isDecreasing(). It checks if any digit is less than the next digit. If yes, set the flag to false and exit from the loop.
- Return the value of the flag variable.






 Java programming
Java programming
Bouncy Number Java Program
BouncyNumberExample1.java
Output 1:
Output 2:
BouncyNumberExample2.java
Output 1:
Output 2:
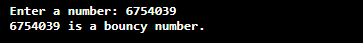
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer