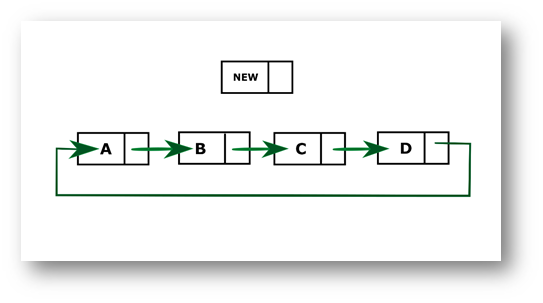
In this program, we create a circular linked list and insert a new node in the middle of the list. If the list is empty, both head and tail will point to new node. If the list is not empty, then we will calculate the size of the list and divide it by 2 to get the mid-point of the list where the new node needs to be inserted.
After inserting the new node in the middle of the list.
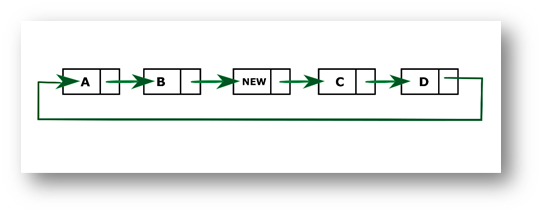
Consider the above diagram; the new node needs to be added to the middle of the list. First, we calculate the size which in this case is 4. So, to get the mid-point, we divide it by 2 and store it in a variable count. We will define two nodes current, and temp such that temp will point to head, and current will point to the node previous to temp. We iterate through the list till mid-point is reached by incrementing temp to temp.next then, insert the new node in between current and temp. Current'next node will be new and the new's next node will be temp.
Algorithm
- Define a Node class which represents a node in the list. It has two properties data and next which will point to the next node.
- Define another class for creating the circular linked list and it has two nodes: head and tail. Variable size stores the size of the list. It has two methods: addInMid() and display() .
- addInMid() will add the node to the middle of the list:
- It first checks whether the head is null (empty list), then it will insert the node as the head.
- Both head and tail will point to the newly added node.
- If the list is not empty, then we calculate size and divide it by 2 to get the mid-point.
- Define node temp that will point to head and current will point to a node previous to temp.
- Iterate through the list until the middle of the list is reached by incrementing temp to temp.next.
- The new node will be inserted after current and before temp such that current will point to the new node and the new node will point to temp.
a. display() will show all the nodes present in the list.
- Define a new node 'current' that will point to the head.
- Print current.data till current will points to head again.
- Current will point to the next node in the list in each iteration.
Program:
Output: