Pandas is a special tool that allows us to perform complex manipulations of data effectively and efficiently. Inside pandas, we mostly deal with a dataset in the form of DataFrame. DataFrames are 2-dimensional data structures in pandas. DataFrames consist of rows, columns, and the data. DataFrame can be created with the help of python dictionaries or lists but in the real world, CSV files are imported and then converted into DataFrames. Sometimes, DataFrames are first written into CSV files. Here, we are going to write a DataFrame into a CSV file.
CSV files:
CSV files or Comma Separated Values files are plain text files but the format of CSV files is tabular. As the name suggests, in a CSV file, each specific value inside the CSV file is generally separated with a comma. The first line identifies the name of a data column. The further subsequent lines identify the values in rows.
Here, the separator character (,) is called the delimiter. There are some more popular delimiters. E.g.: tab(\t), colon (:), semi-colon (;) etc.
We will use DataFrame.to_csv() method to write DataFrame into CSV file. It takes an argument in the form of a DataFrame name which has to be written in a CSV file. It also requires the path of the specified folder where the user wants to create the CSV file.
pandas.DataFrame.to_csv() Method
Write object to a comma-separated values (csv) file.
Syntax:
DataFrame.to_csv(
path_or_buf=None,
sep=',',
na_rep='',
float_format=None,
columns=None,
header=True,
index=True,
index_label=None,
mode='w',
encoding=None,
compression='infer',
quoting=None,
quotechar='"',
line_terminator=None,
chunksize=None,
date_format=None,
doublequote=True,
escapechar=None,
decimal='.',
errors='strict',
storage_options=None
)
# In short
DataFrame.to_csv('path_of_folder\name_of_file')
To work with Python Pandas, we need to import the pandas library. Below is the syntax,
import pandas as pd
Example:
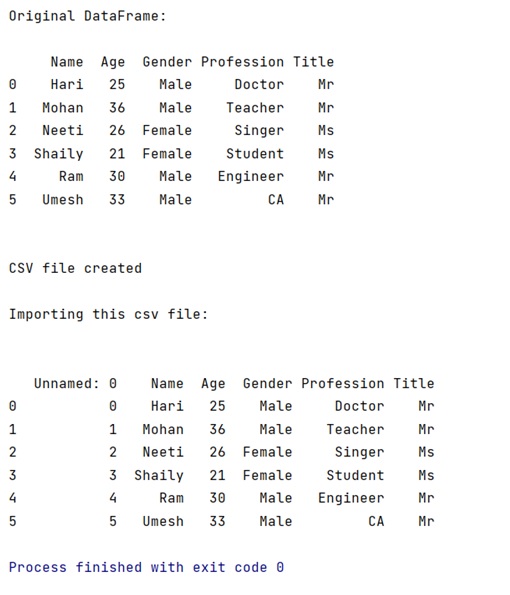
Output:
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer