The two real roots of a quadratic equation ax^2 + bx + c = 0 (where a is nonzero) are given by
belongs to book: MATLAB: A Practical Introduction to Programming and Problem Solving|Stormy Attaway|Fourth Edition| Chapter number:10| Question number:14.10
All Answers
total answers (1)




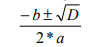 where the discriminant D = b2 – 4*a*c. Write a function to calculate and return the roots of a quadratic equation. Pass the values of a, b, and c to the function. Use a nested function to calculate the discriminant.
where the discriminant D = b2 – 4*a*c. Write a function to calculate and return the roots of a quadratic equation. Pass the values of a, b, and c to the function. Use a nested function to calculate the discriminant. Matlab
Matlab
quadeq.m
function [root1, root2] = quadeq(a,b,c)
% Calculates the roots of a quadratic equation
% ignores potential errors for simplicity
% Format of call: quadeq(a,b,c)
% Returns the two roots
d = discr;
root1 = (-b + sqrt(d))/(2*a);
root2 = (-b - sqrt(d))/(2*a);
function outd = discr
% calculates the discriminant
% Format of call: discr or discr()
% Returns the discriminant
outd = b^2 - 4*a*c;
end % inner function
end % outer function
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer