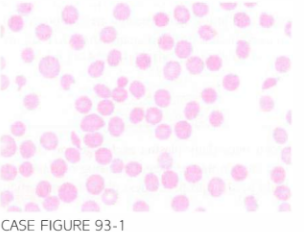
A 39-year-old male patien t is admitted to the ICU with chest pain, slurred speech, and left-sided weakness . Past medical h istory is sign i fican t For hypothyroidism, angina, and bipolar d isorder. Home medications incl ude val proic acid, levothyroxine, and sublingual n itroglyceri n. On physical exam , he is in mild distress, afebri le, and mi ldly hypertensive. Complete blood count shows a leukocyte count of 6,600/,uL, hemoglobin 6.5 g/dl, and platelet count 1 6, 000/,uL. Creatinine is 0.8 mg/dl and LDH is 683 U/L. Troponin level is normal. The peri pheral blood smear is shown below.
Which of the following statements is correct regarding ADAMTS13, the protease which has been found to play a pivotal role in TTP?
- Low ADAMTS 1 3 level predicts a poor response to plasma exchange
- Low ADAMTS 1 3 level identifies patients more likely to relapse early
- Low ADAMTS 1 3 level leads to an excess of small vWF multimers
- Low ADAMTS 1 3 level in acquired TTP is caused by Ig autoantibodies





 Medicine
Medicine
B. Low levels of ADAMTS 13 identify patients at high risk of early relapse; it is not predic-tive of a poor response to plasma exchange. ADAMTS 13, a metalloprotease in plasma, cleaves vWF in plasma, and prevents vWF-mediated platelet aggregation. A deficiency of this protease leads to accu-mulation of ultra-large vWF multimers, which causes microvascular thrombosis in the heart, kidney, spleen, pancreas, adrenal gland, and brain. Such thrombi are composed of platelets and vWF, which is characteristic of TTP. IgG autoantibodies directed against ADAMTS 13 are the primary pathogenetic mechanism involved in acquired TTP (Blood. 20 10; 115:1475-1476).
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer