A 2 2 -year-old H IV-positive male presen ts for Further workup of Fevers , Fatigue. and weigh t loss. Patient reports that he underwen t an extensive workup with no u nderlyi ng etiology determined. Physical examination reveals bilateral cervical and axil lary lymph-adenopathy and no hepatosplenomegaly. Laboratory evaluation reveals hemoglobin of 8. 1 g/dl, leukocyte count of 1 2 .800/,LLL. and platelet count of 1 05 .000/,LLL. Most recent CDLJ cell count is 3 5/ ,LLL. Secondary to the presence of nucleated red blood cells in the peripheral blood . a bone marrow aspirate and biopsy was obtained . Peripheral blood and bone marrow samples are shown below.
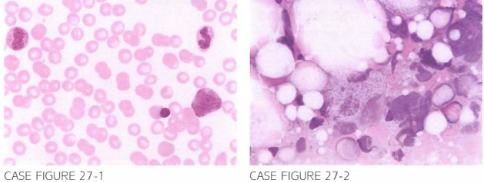
What is the most appropriate step in the workup of this patient?
- Testing bone marrow for the presence of lymphoma
- Testing bone marrow for mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infections
- Flow cytometry of bone marrow aspirate
- Check ferritin level
- Check vitamin B12 level
B. Blood smear shows leukoerythroblastosis, and a foamy macrophage "pseudo-Gaucher" cell is seen in the bone marrow aspirate (noted in above im·age); acid-fast stain (AFB) of the bone marrow aspirate revealed extensive involvement by mycobacteria (as seen below) that on further test-ing was found to represent MAC. MAC is usually a late clinical syndrome in HIV patients with CD4 counts less than 50. Weight loss, fatigue, fever, and anemia are common presenting manifestations in such patients. Several studies examined the clinical benefit and additional yield provided by bone marrow cultures or AFB stains compared with blood cultures alone. One retrospective study showed earlier positivity for bone marrow cultures compared with blood (22 vs. 24 days). Another study re-vealed that blood cultures and blood AFB staining were the most sensitive and quickest method to diagnose disseminated MAC as compared with bone marrow cultures and bone marrow AFB staining (Am J Med. 1 998;104(2):123, Am J Clin Pathol. 1998;1 10(6):806, Int J STD AIDS. 2005;16(10):686).
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer