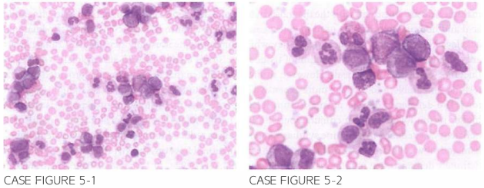
A 6 6-year-old female previously heal thy presen ts for further evaluation of diffuse bone pai n. left-sided abdomi nal discomfort. and progressive fatigue for the last several mon ths. Examination is sign i ficant for splenomegaly, easily palpable below the left costal margin extending to the m idline. Laboratory evaluation reveals leukocyte count of 1 67.000/,LLL. hemoglobi n 9.2 g/dl. and platelet count of 730.000/JLL. Peripheral blood smear is shown.
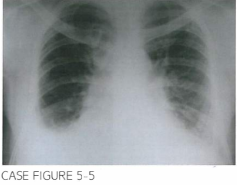
Patien t is started on imatinib LjQO mg daily and is seen for fol low-up 1 month later. Evaluation reveals near-complete normal ization of peripheral blood coun ts. However. patient reports progressively worsening dyspnea on exertion. in addition to periorbital and distal lower extremi ty swelling. Chest x-ray is shown below.
What is the most likely etiology of patient's most recent presentation?
- Leukostasis
- Interstitial lung disease
- Leukemic infiltration
- Fluid overload
- Heart failure
D. Fluid overload manifesting as pulmonary edema, peripheral edema, and periorbital edema is a relatively common side effect of BCR-ABL inhibitors and is thought to be related to inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor receptor, resulting in increased capillary-to-interstitium transport. Leukostasis or leukemic infiltration would be less likely, given the near normalization of peripheral blood counts. Heart failure and interstitial lung disease have been rarely reported with ima-tinib; however, the acute presentation is more consistent with imatinib-induced fluid overload (Cancer Res. 200 1;61 (7):2929).
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer