In Java, there are many ways to swap two numbers. Generally, we use either swap() method of the Math class or use a third (temporary) variable to swap two numbers. Except these two ways, we can also swap two numbers using the bitwise operator (XOR) and using division and multiplication.
In this section, we will focus on creating a Java program to swap two numbers using bitwise operator (^).
Using Bitwise Operator
Bitwise Operator: Bitwise XOR operator is used to swap two numbers. It is represented by the symbol (^). It compares bits of two operands and returns false or 0 if they are equal and returns true or 1 if they are not equal. The truth table of XOR operator is as follows:
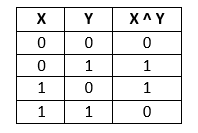
We can use the bitwise XOR operator to swap two numbers without using the swap() method and third variable. We must follow the steps given below:
- Find the binary equivalent of given variables, say X and Y.
- Find X^Y and store it in x, i.e. X = X ^ Y.
- Again, find X^Y and store it in Y, i.e. Y = X ^ Y.
- Find X^Y and store it in X, i.e. X = X ^ Y.
- The numbers are swapped.
Now implement the above steps in an example and understand the swapping.
Example: Swap the variables X = 5 and Y = 9 using the bitwise operator.
Solution:
Step 1: Binary equivalent of the variables X and Y are:
X = 5 = 0101 and Y = 9 = 1001
Step 2: Find X = X ^ Y.
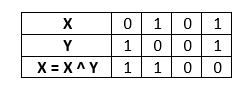
Step 2: Find Y = X ^ Y.
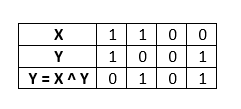
Step 3: Find X = X ^ Y.
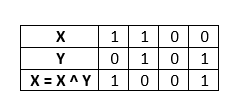
We see that the variable X contains 1001 which is equivalent to 9 and Y contains 0101 which is equivalent to 5. Therefore, the variables X and Y are swapped.
X = 9 and Y = 5
SwapTwoNumbersExample1.java
Output:
Let's create a program that swap two numbers using the function.
SwapTwoNumbersExample2.java
Output:
Using Multiplication and Division
We can also swap two numbers using multiplication and division operator.
SwapTwoNumbersExample3.java
Output: