History
A 37-year-old man presents with a rash and diarrhoea to the haematology out-patient team. Six months previously he had developed red patches on his skin, which then became pale and gradually felt firm and tight. He describes stiffness of his elbow and knee joints, such that he is having trouble straightening his limbs. One year previously he had undergone a matched, unrelated, allogenic bone marrow transplant for acute mye-loid leukaemia. He is taking multiple medications including aciclovir, co-trimoxazole, penicillin V, itraconazole and omeprazole.
Examination
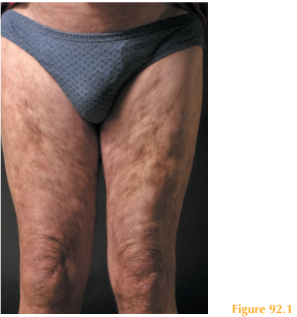
He has extensive skin changes over his trunk and limbs with erythematous patches with hypopigmented centres (Fig. 92.1). There is mottled hyperpigmentation and generalized thickening of the skin, which appears waxy and feels tight. Also, fixed flexion deformities are present over his elbows and knees.
Questions
• What is the diagnosis?
• What other systems can be involved?
• How would you manage this patient?
This patient was diagnosed with chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Skin changes characterized by thickening and tightening after bone marrow transplantation are referred to as sclerodermoid GVHD.
GVHD is an immune disorder that commonly follows bone marrow transplantation. It is less common after solid organ transplantation and, rarely, has also been reported in patients after blood transfusion and by maternal–fetal transfusion. GVHD results from a reaction of incompatible, immunocompetent donor cells against the tissue of an immu-nocompetent host. Acute and chronic disease are described both of which increase the patient’s susceptibility to infection.
Chronic GVHD is said to occur more than 100 days after transplantation. Patients may have had acute GVHD (usually between 14 and 21 days post-transplantation) or it arises de novo. Cutaneous disease has different morphological types. These include lichenoid, sclerodermoid and eczematous types. Lichenoid disease is characterized by flat-topped violaceous ‘lichen–planus’-like papules and plaques, which manifest initially on the extremities but can become generalized. Mucosal disease is also seen. Sclerodermoid dis- ease occurs predominantly over the trunk and upper lower limbs and the skin is described as ‘hardening’ or ‘tight’. This disease can also become generalized leading to joint con-tractures. Hair loss is also a common feature, which is usually permanent.
GVHD may also affect the eyes, mouth, joints, gastrointestional tract (diarrhoea), liver (transaminitis) and respiratory system.
Prevention of GVHD is the mainstay of treatment. Chronic GVHD carries a high morbid-ity and mortality. It is commonly associated with recurrent and occasionally fatal bacte-rial infections, which are the main cause of death in patients with GVHD. Patients are immunosuppressed with a variety of medication including ciclosporin, mycophenolate and tacrolimus with or without prednisone.
Managing skin GVHD is dependent on the extent and affected site. For limited disease topical therapy with potent corticosteroids can be of benefit. For more extensive dis-ease the aim is to treat GVHD before life-threatening sepsis occurs. High-dose systemic corticosteroids are usually added to the immunosuppressant regime. Phototherapy with psoralen–UVA and high-dose long-wave ultraviolet (UV) radiation (UVA1) may reduce the severity of the cutaneous skin problems. In addition, to reduce the amount of immu- nosuppression required, extracorporeal photophoresis can be effective.
KEY POINTS
• Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is an immune disorder that may occur after bone marrow transplantation.
• Acute and chronic forms of GVDH have been described.
• Different types of cutaneous GVHD include lichenoid, sclerodermoid and eczematous.
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer