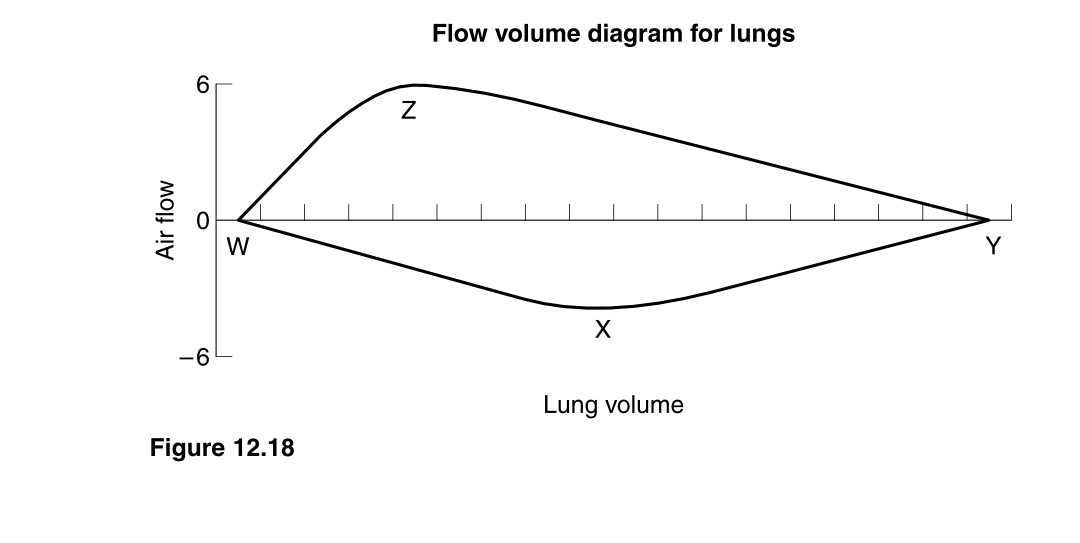
Figure 12.18 shows four points on the flow–volume diagram of the lungs of a healthy young man. W is the lung volume at total lung capacity and Y is the lung volume at residual volume. Z and X represent maximal outflow and maximal inflow respectively. The person has breathed in and out a vital capacity as quickly as possible. For each of descriptions a–e below, select the best option from the following list of points, lines and areas.
1. W
2. X
3. Y
4. Z
5. WZ
6. ZW
7. ZY
8. YZ
9. WX
10. XW
11. XY
12. YX
13. ZX
14. XZ
15. Totally inside the loop below.
16. Partially outside the loop below
- The line which corresponds most closely to the first part of a forced expiratory volume in one second manoeuvre.
- The point at which lung volume is closest to one litre.
- The position of the loop during strenuous exercise in the same person.
- The final part of the manoeuvre of measuring a fast vital capacity.
- The point at which intra-alveolar pressure is likely to be most negative.





 Medicine
Medicine
a. Option 5 WZ. The manoeuvre starts at total lung capacity and the volume expired in the first second is measured.
b. Option 3 Y. The residual volume of a healthy young man is usually a little over a litre.
c. Option 15 Totally inside the loop. Although volumes and flows increase with exercise, they are still below the maximal; the loop for tidal breathing is smaller still.
d. Option 7 ZY. After the first second of rapid expiration the person must continue breathing out until residual volume is reached, usually in a further second or two.
e. Option 2 X. This is the point of maximal inflow; at this point the pressure gradient between atmosphere and alveoli is also maximal, with alveolar pressure subatmospheric.
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer