(Test whether a graph is connected) Write a program that reads a graph from a file and determines whether the graph is connected. The first line in the file contains a number that indicates the number of vertices (n). The vertices are labeled as 0, 1, . . . , n-1. Each subsequent line, with the format u v1 v2 ..., describes edges (u, v1), (u, v2), and so on. Figure 28.21 gives the examples of two files for their corresponding graphs.
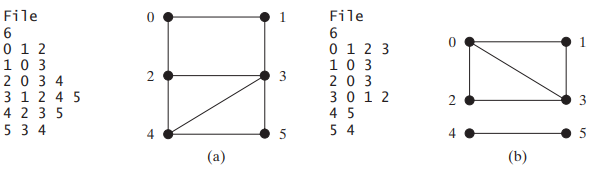
FIGURE 28.21 The vertices and edges of a graph can be stored in a file.
Your program should prompt the user to enter the name of the file, then it should read data from the file, create an instance g of UnweightedGraph, invoke g.printEdges() to display all edges, and invoke dfs() to obtain an instance tree of AbstractGraph.Tree. If tree.getNumberOfVerticesFound() is the same as the number of vertices in the graph, the graph is connected. Here is a sample run of the program:
Enter a file name: c:\exercise\GraphSample1.txt
number of vertices is 6
Vertex 0: (0, 1) (0, 2)
Vertex 1: (1, 0) (1, 3)
Vertex 2: (2, 0) (2, 3) (2, 4)
Vertex 3: (3, 1) (3, 2) (3, 4) (3, 5)
Vertex 4: (4, 2) (4, 3) (4, 5)
Vertex 5: (5, 3) (5, 4)
The graph is connected
(Hint: Use new UnweightedGraph(list, numberOfVertices) to create a graph, where list contains a list of AbstractGraph.Edge objects. Use new AbstractGraph.Edge(u, v) to create an edge. Read the first line to get the number of vertices. Read each subsequent line into a string s and use s.split("[\\s+]") to extract the vertices from the string and create edges from the vertices.)





 Java programming
Java programming
Exercise_28_01.java
Graph.java
UnweightedGraph.java
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer