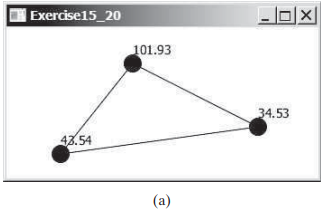
(Geometry: display angles) Write a program that enables the user to drag the vertices of a triangle and displays the angles dynamically as the triangle shape changes, as shown in Figure 15.30a
belongs to book: Introduction to Java Programming, Comprehensive Version (10th Edition)|Y. Danial liang|10th edition| Chapter number:15| Question number:20
All Answers
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer
total answers (1)




 Java programming
Java programming