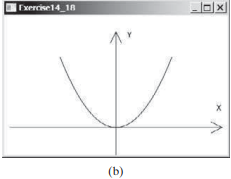
(Plot the square function) Write a program that draws a diagram for the function f(x) = x2 (see Figure 14.48b)
belongs to book: Introduction to Java Programming, Comprehensive Version (10th Edition)|Y. Danial liang|10th edition| Chapter number:14| Question number:18
All Answers
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer
total answers (1)




 Java programming
Java programming