(Geometry: the Circle2D class) Define the Circle2D class that contains:
■ Two double data fields named x and y that specify the center of the circle with getter methods.
■ A data field radius with a getter method.
■ A no-arg constructor that creates a default circle with (0, 0) for (x, y) and 1 for radius.
■ A constructor that creates a circle with the specified x, y, and radius.
■ A method getArea() that returns the area of the circle.
■ A method getPerimeter() that returns the perimeter of the circle.
■ A method contains(double x, double y) that returns true if the specified point (x, y) is inside this circle (see Figure 10.21a).
■ A method contains(Circle2D circle) that returns true if the specified circle is inside this circle (see Figure 10.21b).
■ A method overlaps(Circle2D circle) that returns true if the specified circle overlaps with this circle (see Figure 10.21c).
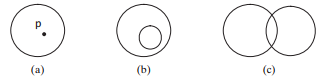
FIGURE 10.21 (a) A point is inside the circle. (b) A circle is inside another circle. (c) A circle
overlaps another circle.
Draw the UML diagram for the class and then implement the class. Write a test program that creates a Circle2D object c1 (new Circle2D(2, 2, 5.5)), displays its area and perimeter, and displays the result of c1.contains(3,3), c1.contains(new Circle2D(4, 5, 10.5)), and c1.overlaps(new Circle2D(3, 5, 2.3)).





 Java programming
Java programming
Circle2D.java
need an explanation for this answer? contact us directly to get an explanation for this answer