(Financial tsunami) Banks lend money to each other. In tough economic times, if a bank goes bankrupt, it may not be able to pay back the loan. A bank’s total assets are its current balance plus its loans to other banks. The diagram in Figure 8.8 shows five banks. The banks’ current balances are 25, 125, 175, 75, and 181 million dollars, respectively. The directed edge from node 1 to node 2 indicates that bank 1 lends 40 million dollars to bank 2.
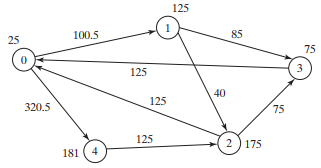
FIGURE 8.8 Banks lend money to each other.
If a bank’s total assets are under a certain limit, the bank is unsafe. The money it borrowed cannot be returned to the lender, and the lender cannot count the loan in its total assets. Consequently, the lender may also be unsafe, if its total assets are under the limit. Write a program to find all the unsafe banks. Your program reads the input as follows. It first reads two integers n and limit, where n indicates the number of banks and limit is the minimum total assets for keeping a bank safe. It then reads n lines that describe the information for n banks with IDs from 0 to n-1.
The first number in the line is the bank’s balance, the second number indicates the number of banks that borrowed money from the bank, and the rest are pairs of two numbers. Each pair describes a borrower. The first number in the pair is the borrower’s ID and the second is the amount borrowed. For example, the input for the five banks in Figure 8.8 is as follows (note that the limit is 201):
5 201
25 2 1 100.5 4 320.5
125 2 2 40 3 85
175 2 0 125 3 75
75 1 0 125
181 1 2 125
The total assets of bank 3 are (75 + 125), which is under 201, so bank 3 is unsafe. After bank 3 becomes unsafe, the total assets of bank 1 fall below (125 + 40). Thus, bank 1 is also unsafe. The output of the program should be
Unsafe banks are 3 1
(Hint: Use a two-dimensional array borrowers to represent loans. borrowers[i][j] indicates the loan that bank i loans to bank j. Once bank j becomes unsafe, borrowers[i][j] should be set to 0.)





 Java programming
Java programming